分子隧道电离电子波包的相位结构
强激光场下原子分子隧道电离是强场物理的基本问题, 对光场调控原子分子动力学有着重要影响,比如电子关联和高次谐波产生等。理论上精确描述在强激光场作用下分子隧道电离是非常困难的(见示意图1),人们对从分子隧道电离电子波包的特征缺少深入认识,通常近似地认为分子隧道电离的电子波包为平面波。
图1:氧气分子在强激光场中的隧道电离示意图
最近,北京大学物理学院人工微结构和介观物理国家重点实验室“极端光学创新研究团队“刘运全教授和龚旗煌院士等在《物理评论快报》发表了标题为“Phase Structure of Strong-Field Tunneling Wave Packets from Molecules”的研究论文[Physical Review Letters 116, 163004(2016)]。团队成员创新性提出了分子隧道电离的量子轨迹蒙特卡洛理论(Molecular-Quantum-Trajectory Monte Carlo theory),解析地给出了分子坐标系下隧道电离率,揭示取向分子隧道电离的电子波包存在初始相位,进一步通过他们发展的蒙特卡洛模拟和费曼路径积分的方法[M. Li et al., Phys. Rev. Lett.112, 113002(2014)],计算得到分子坐标系下的光电子角分布。解释了实验上观测到取向氮气分子的不对称的归一化动量角分布以及预测了取向O2分子的光电子角分布。
结果表明,分子坐标系下的光电子角分布依赖分子外层轨道的电子云分布(氮气分子的外层轨道为sg, 氧气分子的外层轨道为pg),隧道电离电子波包的初始相位以及分子轴相对与激光偏振轴的取向角度,并可以广泛应用于多原子分子的隧道电离问题。该研究成果揭示了分子隧道电离的电子波包相位,对光电子全息成像、高次谐波成像、以及超快量子调控方面等方面具有重要应用。
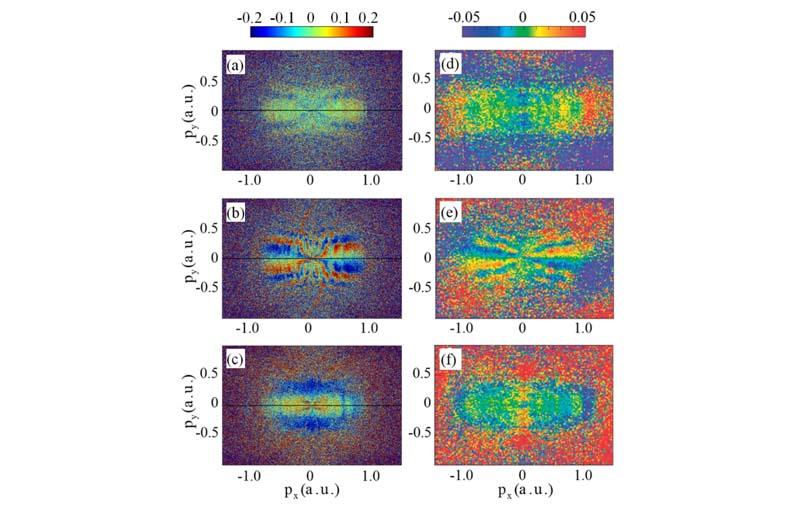
(左)理论上计算得到N2分子在分子轴与激光偏振轴夹角为0度,45度和90度下的归一化动量角分布。(右)图为实验结果。
论文第一作者为二年级博士生刘明明同学。该研究得到国家重大科学研究计划、国家自然科学基金重点项目、量子物质科学协同创新中心以及介观物理与人工微结构国家重点实验室等资助。
Phase Structure of Strong-Field Tunneling Wave Packets from Molecules
Recently,the team of extreme optics, Prof. Yunquan Liu and Prof. Qihuang Gong, have study the phase structure of the tunneling wave packets from strong-field ionization of molecules and present a molecular quantum-trajectory Monte Carlo (MO-QTMC) model to describe the laser-driven dynamics of electron process in molecules. Using this model, they reproduce and explain the alignment-dependent molecular frame photoelectron spectra of strong-field tunneling ionization of N2 reported by M. Meckel et al. [Nat. Phys. 10, 594(2014)]. Besides modelling the low-energy photoelectron angular distributions quantitatively, we extract the phase structure of strong-field molecular tunneling wave packets, shedding light on its physical origin. The initial phase of the tunneling wave packets at the tunnel exit depends on both, the initial transverse momentum distribution and the molecular internuclear distance. It has been further shown that the ionizing molecular orbital has a critical effect on the initial phase of the tunneling wave packets. Since the phase structure of photoelectron wave packet is a key ingredient, this work has important implication for modelling strong-field molecular photoelectron holography, high-harmonic generation and molecular orbital imaging.